Badminton Rules & Scoring

The best sport in the whole world is beautiful to play and watch. So try it yourself! But to fully enjoy Badminton, you should understand everything about it. There are rules and guidelines that are important to know. So that`s exactly what I will discuss in this blog post, among some other facts and hints. So here is what you`ll get:
- Badminton Rules & Scoring
- Badminton Court
- Badminton Terms
- Badminton Records
By the way, if you have any kind of question about badminton rules or even a remark about the badminton terms or records, feel free to leave a comment and I will gladly try to answer your question!
Everything you need to know about Badminton
Badminton Rules & Scoring
Badminton Scoring

A badminton match is played in “Best of 3” format, which means that who manages to win two games, wins the whole match. If after two games both sides have one game each, a third and deciding game is played.
Since 2006 a badminton match is played in the “rally point system”. This means a game is won when one side gets to 21 points. Each point counts, regardless of who is serving. The very first serve of a match is decided by coin toss, after that the winner of the last exchange has the serve.
If the scoreboard shows 20:20, extra points are required until there is a two point winning margin – until they get to 29:29. In that rare case, the next point decides the game even without a two point winning margin.
Serving is done from the right side of the court on even numbers; from the left side of the court on uneven numbers – always directed diagonally to the service area across the net.
Badminton Doubles Rules
Serve: Inner back line – Outer side line – Service line
Ball in play: Back line – Outer side line
In Doubles the outer sidelines are significant at all times. The backline however is only valid when the rally is going. During the service situation the long service line for Doubles must not be passed by the shuttle. Additionally the shuttle must pass the short service line for Doubles.
Badminton Singles Rules
Serve: Back line – Inner side line – Service line
Ball in play: Back line – Inner side line
In Singles the inner sidelines are significant, as well as the backline. During the service situation the shuttle must pass the short service line. Other than that there are no exceptions in Singles.
Badminton Service Rules
The serve in badminton has very strict rules. It has to be played while standing still within the service are. The racket has to point in a downward direction and the racket head must not exceed the player`s “hip height”. This is of course something that differs for each player and allows everyone to serve comfotably in recognition of the individual body height.
However this rule is often bended by professional players as much as possible and quite often results in service faults called by the referees. Especially on flick serves players tend to strike the shuttle to high.
Equipment Rules
Apart from specific badminton shoes that are allowed for use on a badminton court and also fulfil the specific needs for badminton movements, the equipment rules are directed mostly at the badminton racket:
- A badminton racket consists of a handle connected to a shaft which is again connected to a racket head. The racket head must not be bigger than 280mm in length and 220mm in width.
- In total a racket must not exceed a length of 680mm and a width of 230mm.
- A racket has to be strung with interwoven synthetic strings and the full racket weight (strings included) must be at least 80g and not exceed 100g.
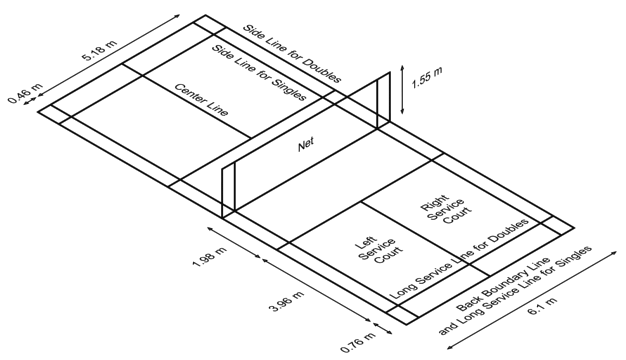
Badminton Court
The original uploader was Ciantic at English Wikipedia. [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Badminton is definitely an indoor sport, because even the slightest bit of wind can make it very hard to hit the shuttle correctly. Luckily indoors you`ll find enough locations with the badminton court lines already painted on the floor. The Badminton court dimensions vary depending on whether you play Singles or Doubles. What they have in common is that the lines are always part of the court. Even if you hit just the smallest fraction of the outer sideline, you win the rally.
Court Dimensions
Singles
In singles matches the inner sidelines are valid and therefore the court has a width of 5.18m. The length is 13.40m for both sides of the court combined. So each player has to cover a length of 6.70m.
Doubles
In doubles matches the court length is of course the same – apart from service situation. The court however is wider, because the outer sidelines apply. That makes for a width of 6.10m, which accomodates the fact that in Doubles you have to players to cover the whole court instead of just one.
Badminton net height
The badminton net should always have a height of 1.55m. This is the height that should be measured on the net posts. Depending on how hard the net is spanned, it will be a little lower in the middle. 1.524m is stated within the official rules.
Badminton Terms
![]()
Serve
The initial stroke to start a rally.
Short serve / Long serve
The player to serve pretty much has two options. A short serve, which is the most popular choice among professional players, especially in Doubles Disciplines. Simply because you don`t give away a free lift and there the attack. The long serve -also called a swip serve- is often used as a surprise element, because the returning player will usually stand very close to the net, expecting the short serve and ready to pounce on it. With all body weight put forward, it`s not easy to get back in time to reach a good swip.
Return
The second shot of a rally, returning the service. Should be as agressive as possible to get the upper hand immediately. Statistics prove that in Doubles the first pair that provokes a lifting of the shutlle, will likely win the point.
Third Shot
The first three shots have become incredibly important in Badminton, they set the tone of the rallies. The master of these situations is Hendra Setiawan from Indonesia.
Interception
Being able to get to a fast and flat shot that was intended to fly to the backcourt – and more importantly hit it as a winner. Very quick hand, reactions and anticipation are needed for a successful interception. Again a speciality of Hendra Setiawan. Kevin Sanjaja Sukamuljo is very gifted here as well.
Game Point
The opportunity to win the first or second game with the next point that is played. At least 20 points are needed for this. In the third and deciding game it could only be a…
Match Point
The opportunity to win the whole match with the next point. Can occur in the second or third set.
Smash
Important attacking shot to decide a rally. Should be hit at the highest point possible in a downward direction. The speed of the smash is defined by the arm accelaration, finger work, shoulder rotation and how mich you can put your body into it.
Jump smash
A smash that is being hit at the highest point of a big leap into the air. Very effective because you can generate a better angle and hit a very steep smash.
Stick Smash
A smash that is being hit without the full body weight behind the stroke. So a smash where the power is generated just by the arm and wrist.
Body smash
A good player will think about the direction of the smash, which is even more importand than the smash speed. Often you would go for the sidelines. But there is a risk of hitting the shuttle wide then, plus the opponent will expect that. A smash into the body however is often very unexpected and very hard to defend. So it`s a good option to leave the opponent thinking about the placement.
Clear
A rally shot, hit very high and long to the backline. Often used to get out of trouble. Can be an attacking shot as well, if it is being played a little less high and faster in situations, where the opponent usually would expect a smash.
Drop
Rather slow shot, hit from the back court to the net. At best should fall as close as possible behind the net. Can be played sharper at the expense of getting longer than desired. Slicing the shuttle very hard can be effective for drops as well, because that way you can generate a very steep flying curve with more speed than a usual drop and still produce a very good angle to make it fall closely behind the net.
Deception
Trying to play a different shot than the opponent expects by changing or disguising the shot preparation. This could be a different arm movement ahead of the stroke, holding the shot a split second longer, before performing it or even a look in another direction. Anything really that leaves the opponent surprised.
Lift
A defensive shot played from far below the tape far and high to the backline.
Drive
Flat and fast shots played at shoulder height almost straight to the other side.
Cross
Playing the shuttle diagonally to the other court side. Can be used for any shot, cross smash, cross drop etc. and is possibly very effective. However in some situations tactically not the best options. Especially in doubles a cross smash can open the whole court for the opponent (and is easier to defend beccause there is more time until the shuttle reached the other player).
Tumble / Tumbling netshot
A net shot where you make the shuttle spin by cutting under it with your racket. Very effective, because it is almost impossible for the opponent to play a controlled shot while the birdie is tumbling. He has to wait until it has stopped tumbling, which is usually far below the tape.
Reverse slice
Slicing the shuttle gives it a very sharp flying curve. This can be even better, if you hit the slice to the opposite direction as the slicing motion with the racket would suggest. This demands a very good technique, as it is one of the most complicated strokes in Badminton. While we`re at that: Tai Tzu Yings Reverse Slice Deceptive Backhand Drops is one of the most extraordinary shots I have ever seen.
Hawk-Eye / Challenge
An electronic system that can validate, if a line call was correct or not. As good as a linesman may be, the human eye can not always see correctly, if a shuttle was in or out. After all a badminton shuttle can reach more than 300km/h. So in professional tournaments the players have to challenges per game, which they can use to have a decision checked. If the players challenge was successful, they keep their number of challenges. If the player was wrong to challenge, they loose one of their chances.
Shuttle / Birdie
The “ball” in Badminton. Manufactured from 16 goosefeathers stuck into a cork, with very unique flying characteristics.
Have a look at this post to learn more about badminton shuttlecocks.
Backhand Grip
For backhand shots you should in most cases quickly change your grip. Instead of the V grip, turn it with your fingers until you can put the thumb onto the flat/broad side of the racket grip. This will give you an extra amount of power in your backhand shots.
Badminton Records
The fastest smash in official competition
Mads Pieler Kolding (Denmark) in Indian Premier League 2017:
426 kp/h
The longest rally in an official badminton match
Tien Minh Nguyen vs. Jan O. Jorgensen – QF of WC 2013:
2 minutes long rally with 108 shots
Longest badminton marathon of playing singles
Thomas Paulweber & Mario Langmann in Austria 2016:
25h 25min 44sec
Professional player with most super series titles ever
Lee Chong Wei (Malaysia):
46 titles in mens singles competition

One Comment